All The Things You Will Need To Understand About Heel Pain
Overview

Plantar fasciitis is a painful condition affecting the bottom of the foot. It is a common cause of Heel Pain and is sometimes called a heel spur. Plantar fasciitis is the correct term to use when there is active inflammation. Plantar fasciosis is more accurate when there is no inflammation but chronic degeneration instead. Acute plantar fasciitis is defined as inflammation of the origin of the plantar fascia and fascial structures around the area. Plantar fasciitis or fasciosis is usually just on one side. In about 30 per cent of all cases, both feet are affected. This guide will help you understand how plantar fasciitis develops, how the condition causes problems, what can be done for your pain.
Causes
Heel pain can have many causes. If your heel hurts, see your primary care doctor or orthopaedic foot and ankle specialist right away to determine why and get treatment. Tell him or her exactly where you have pain and how long you've had it. Your doctor will examine your heel, looking and feeling for signs of tenderness and swelling. You may be asked to walk, stand on one foot or do other physical tests that help your doctor pinpoint the cause of your sore heel. Conditions that cause heel pain generally fall into two main categories: pain beneath the heel and pain behind the heel.
Symptoms
Plantar fasciitis is a condition of irritation to the plantar fascia, the thick ligament on the bottom of your foot. It classically causes pain and stiffness on the bottom of your heel and feels worse in the morning with the first steps out of bed and also in the beginning of an activity after a period of rest. For instance, after driving a car, people feel pain when they first get out, or runners will feel discomfort for the first few minutes of their run. This occurs because the plantar fascia is not well supplied by blood, which makes this condition slow in healing, and a certain amount of activity is needed to get the area to warm up. Plantar fasciitis can occur for various reasons: use of improper, non-supportive shoes; over-training in sports; lack of flexibility; weight gain; prolonged standing; and, interestingly, prolonged bed rest.
Diagnosis
After you have described your foot symptoms, your doctor will want to know more details about your pain, your medical history and lifestyle, including. Whether your pain is worse at specific times of the day or after specific activities. Any recent injury to the area. Your medical and orthopedic history, especially any history of diabetes, arthritis or injury to your foot or leg. Your age and occupation. Your recreational activities, including sports and exercise programs. The type of shoes you usually wear, how well they fit, and how frequently you buy a new pair. Your doctor will examine you, including. An evaluation of your gait. While you are barefoot, your doctor will ask you to stand still and to walk in order to evaluate how your foot moves as you walk. An examination of your feet. Your doctor may compare your feet for any differences between them. Then your doctor may examine your painful foot for signs of tenderness, swelling, discoloration, muscle weakness and decreased range of motion. A neurological examination. The nerves and muscles may be evaluated by checking strength, sensation and reflexes. In addition to examining you, your health care professional may want to examine your shoes. Signs of excessive wear in certain parts of a shoe can provide valuable clues to problems in the way you walk and poor bone alignment. Depending on the results of your physical examination, you may need foot X-rays or other diagnostic tests.
Non Surgical Treatment
The following steps may help relieve your heel pain. Use crutches to take weight off your feet. Rest as much as possible for at least a week. Apply ice to the painful area. Do this at least twice a day for 10 to 15 minutes, more often in the first couple of days. Take acetaminophen or ibuprofen for pain. Wear proper-fitting shoes. Use a heel cup, felt pads in the heel area, or shoe insert. Wear night splints. Your doctor may recommend other treatments, depending on the cause of your heel pain.
Surgical Treatment
With the advancements in technology and treatments, if you do need to have surgery for the heel, it is very minimal incision that?s done. And the nice thing is your recovery period is short and you should be able to bear weight right after the surgery. This means you can get back to your weekly routine in just a few weeks. Recovery is a lot different than it used to be and a lot of it is because of doing a minimal incision and decreasing trauma to soft tissues, as well as even the bone. So if you need surgery, then your recovery period is pretty quick.
Prevention

Wear properly fitting shoes. Place insoles or inserts in your shoes to help control abnormal foot motion. Maintain a healthy weight. Exercise and do foot stretches as they have been shown to decrease the incidence of heel pain.

Plantar fasciitis is a painful condition affecting the bottom of the foot. It is a common cause of Heel Pain and is sometimes called a heel spur. Plantar fasciitis is the correct term to use when there is active inflammation. Plantar fasciosis is more accurate when there is no inflammation but chronic degeneration instead. Acute plantar fasciitis is defined as inflammation of the origin of the plantar fascia and fascial structures around the area. Plantar fasciitis or fasciosis is usually just on one side. In about 30 per cent of all cases, both feet are affected. This guide will help you understand how plantar fasciitis develops, how the condition causes problems, what can be done for your pain.
Causes
Heel pain can have many causes. If your heel hurts, see your primary care doctor or orthopaedic foot and ankle specialist right away to determine why and get treatment. Tell him or her exactly where you have pain and how long you've had it. Your doctor will examine your heel, looking and feeling for signs of tenderness and swelling. You may be asked to walk, stand on one foot or do other physical tests that help your doctor pinpoint the cause of your sore heel. Conditions that cause heel pain generally fall into two main categories: pain beneath the heel and pain behind the heel.
Symptoms
Plantar fasciitis is a condition of irritation to the plantar fascia, the thick ligament on the bottom of your foot. It classically causes pain and stiffness on the bottom of your heel and feels worse in the morning with the first steps out of bed and also in the beginning of an activity after a period of rest. For instance, after driving a car, people feel pain when they first get out, or runners will feel discomfort for the first few minutes of their run. This occurs because the plantar fascia is not well supplied by blood, which makes this condition slow in healing, and a certain amount of activity is needed to get the area to warm up. Plantar fasciitis can occur for various reasons: use of improper, non-supportive shoes; over-training in sports; lack of flexibility; weight gain; prolonged standing; and, interestingly, prolonged bed rest.
Diagnosis
After you have described your foot symptoms, your doctor will want to know more details about your pain, your medical history and lifestyle, including. Whether your pain is worse at specific times of the day or after specific activities. Any recent injury to the area. Your medical and orthopedic history, especially any history of diabetes, arthritis or injury to your foot or leg. Your age and occupation. Your recreational activities, including sports and exercise programs. The type of shoes you usually wear, how well they fit, and how frequently you buy a new pair. Your doctor will examine you, including. An evaluation of your gait. While you are barefoot, your doctor will ask you to stand still and to walk in order to evaluate how your foot moves as you walk. An examination of your feet. Your doctor may compare your feet for any differences between them. Then your doctor may examine your painful foot for signs of tenderness, swelling, discoloration, muscle weakness and decreased range of motion. A neurological examination. The nerves and muscles may be evaluated by checking strength, sensation and reflexes. In addition to examining you, your health care professional may want to examine your shoes. Signs of excessive wear in certain parts of a shoe can provide valuable clues to problems in the way you walk and poor bone alignment. Depending on the results of your physical examination, you may need foot X-rays or other diagnostic tests.
Non Surgical Treatment
The following steps may help relieve your heel pain. Use crutches to take weight off your feet. Rest as much as possible for at least a week. Apply ice to the painful area. Do this at least twice a day for 10 to 15 minutes, more often in the first couple of days. Take acetaminophen or ibuprofen for pain. Wear proper-fitting shoes. Use a heel cup, felt pads in the heel area, or shoe insert. Wear night splints. Your doctor may recommend other treatments, depending on the cause of your heel pain.
Surgical Treatment
With the advancements in technology and treatments, if you do need to have surgery for the heel, it is very minimal incision that?s done. And the nice thing is your recovery period is short and you should be able to bear weight right after the surgery. This means you can get back to your weekly routine in just a few weeks. Recovery is a lot different than it used to be and a lot of it is because of doing a minimal incision and decreasing trauma to soft tissues, as well as even the bone. So if you need surgery, then your recovery period is pretty quick.
Prevention

Wear properly fitting shoes. Place insoles or inserts in your shoes to help control abnormal foot motion. Maintain a healthy weight. Exercise and do foot stretches as they have been shown to decrease the incidence of heel pain.
The Main Causes And Treatment Plans For Achilles Tendonitis Suffering
Overview
 The Achilles is a large tendon that connects two major calf muscles to the back of the heel bone. If this tendon is overworked and tightens, the collagen fibres of the tendon may break, causing inflammation and pain. This can result in scar tissue formation, a type of tissue that does not have the flexibility of tendon tissue. Four types of Achilles injuries exist, 1) Paratendonitis - involves a crackly or crepitus feeling in the tissues surrounding the Achilles tendon. 2) Proliferative Tendinitis - the Achilles tendon thickens as a result of high tension placed on it. 3) Degenerative Tendinitis - a chronic condition where the Achilles tendon is permanently damaged and does not regain its structure. 4) Enthesis - an inflammation at the point where the Achilles tendon inserts into the heel bone.
The Achilles is a large tendon that connects two major calf muscles to the back of the heel bone. If this tendon is overworked and tightens, the collagen fibres of the tendon may break, causing inflammation and pain. This can result in scar tissue formation, a type of tissue that does not have the flexibility of tendon tissue. Four types of Achilles injuries exist, 1) Paratendonitis - involves a crackly or crepitus feeling in the tissues surrounding the Achilles tendon. 2) Proliferative Tendinitis - the Achilles tendon thickens as a result of high tension placed on it. 3) Degenerative Tendinitis - a chronic condition where the Achilles tendon is permanently damaged and does not regain its structure. 4) Enthesis - an inflammation at the point where the Achilles tendon inserts into the heel bone.
Causes
Achilles tendinitis can be caused by any activity that puts stress on your Achilles tendon. Tendinitis can develop if you run or jump more than usual or exercise on a hard surface. Tendinitis can be caused by shoes that do not fit or support your foot and ankle. Tight tendons and muscles, You may have tight hamstring and calf muscles in your upper and lower leg. Your tendons also become stiffer and easier to injure as you get older. Arthritis, Bony growths caused by arthritis can irritate the Achilles tendon, especially around your heel.
Symptoms
If you have Achilles tendinitis or Achilles enthesopathy, you are likely to experience the following symptoms. Pain. You may notice aching, burning, or tearing pains at the back of your heel or above the ankle. The pain can range from mild to very severe and disabling. It is most noticeable in the following circumstances. After resting. Many people report that pain increases when they first get out of bed in the morning or after sitting for a period of time. After exercise. Pain may increase if you exercise or stand for a period of time. A lump. In some cases, a tender lump can develop at the site of the injured tendon (tendinosis). Bone spurs. When the injury occurs at the point where the tendon attaches to the foot, a bone spur may develop on the heel.
Diagnosis
Studies such as x-rays and MRIs are not usually needed to make the diagnosis of tendonitis. While they are not needed for diagnosis of tendonitis, x-rays may be performed to ensure there is no other problem, such as a fracture, that could be causing the symptoms of pain and swelling. X-rays may show evidence of swelling around the tendon. MRIs are also good tests identify swelling, and will show evidence of tendonitis. However, these tests are not usually needed to confirm the diagnosis; MRIs are usually only performed if there is a suspicion of another problem that could be causing the symptoms. Once the diagnosis of tendonitis is confirmed, the next step is to proceed with appropriate treatment. Treatment depends on the specific type of tendonitis. Once the specific diagnosis is confirmed, the appropriate treatment of tendonitis can be initiated.
Nonsurgical Treatment
The recommended treatment for Achilles tendinitis consists of icing, gentle stretching, and modifying or limiting activity. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or aspirin, can reduce pain and swelling. Physical therapy and the use of an orthotic (heel lift) can also be helpful. For chronic cases where tendinosis is evident and other methods of treatment have failed, surgery may be recommended to remove and repair the damaged tissue.

Surgical Treatment
Surgery is considered the last resort and is often performed by an orthopedic surgeon. It is only recommended if all other treatment options have failed after at least six months. In this situation, badly damaged portions of the tendon may be removed. If the tendon has ruptured, surgery is necessary to re-attach the tendon. Rehabilitation, including stretching and strength exercises, is started soon after the surgery. In most cases, normal activities can be resumed after about 10 weeks. Return to competitive sport for some people may be delayed for about three to six months.
Prevention
To prevent Achilles tendonitis or tendonosis from recurring after surgical or non-surgical treatment, the foot and ankle surgeon may recommend strengthening and stretching of the calf muscles through daily exercises. Wearing proper shoes for the foot type and activity is also important in preventing recurrence of the condition.
 The Achilles is a large tendon that connects two major calf muscles to the back of the heel bone. If this tendon is overworked and tightens, the collagen fibres of the tendon may break, causing inflammation and pain. This can result in scar tissue formation, a type of tissue that does not have the flexibility of tendon tissue. Four types of Achilles injuries exist, 1) Paratendonitis - involves a crackly or crepitus feeling in the tissues surrounding the Achilles tendon. 2) Proliferative Tendinitis - the Achilles tendon thickens as a result of high tension placed on it. 3) Degenerative Tendinitis - a chronic condition where the Achilles tendon is permanently damaged and does not regain its structure. 4) Enthesis - an inflammation at the point where the Achilles tendon inserts into the heel bone.
The Achilles is a large tendon that connects two major calf muscles to the back of the heel bone. If this tendon is overworked and tightens, the collagen fibres of the tendon may break, causing inflammation and pain. This can result in scar tissue formation, a type of tissue that does not have the flexibility of tendon tissue. Four types of Achilles injuries exist, 1) Paratendonitis - involves a crackly or crepitus feeling in the tissues surrounding the Achilles tendon. 2) Proliferative Tendinitis - the Achilles tendon thickens as a result of high tension placed on it. 3) Degenerative Tendinitis - a chronic condition where the Achilles tendon is permanently damaged and does not regain its structure. 4) Enthesis - an inflammation at the point where the Achilles tendon inserts into the heel bone.
Causes
Achilles tendinitis can be caused by any activity that puts stress on your Achilles tendon. Tendinitis can develop if you run or jump more than usual or exercise on a hard surface. Tendinitis can be caused by shoes that do not fit or support your foot and ankle. Tight tendons and muscles, You may have tight hamstring and calf muscles in your upper and lower leg. Your tendons also become stiffer and easier to injure as you get older. Arthritis, Bony growths caused by arthritis can irritate the Achilles tendon, especially around your heel.
Symptoms
If you have Achilles tendinitis or Achilles enthesopathy, you are likely to experience the following symptoms. Pain. You may notice aching, burning, or tearing pains at the back of your heel or above the ankle. The pain can range from mild to very severe and disabling. It is most noticeable in the following circumstances. After resting. Many people report that pain increases when they first get out of bed in the morning or after sitting for a period of time. After exercise. Pain may increase if you exercise or stand for a period of time. A lump. In some cases, a tender lump can develop at the site of the injured tendon (tendinosis). Bone spurs. When the injury occurs at the point where the tendon attaches to the foot, a bone spur may develop on the heel.
Diagnosis
Studies such as x-rays and MRIs are not usually needed to make the diagnosis of tendonitis. While they are not needed for diagnosis of tendonitis, x-rays may be performed to ensure there is no other problem, such as a fracture, that could be causing the symptoms of pain and swelling. X-rays may show evidence of swelling around the tendon. MRIs are also good tests identify swelling, and will show evidence of tendonitis. However, these tests are not usually needed to confirm the diagnosis; MRIs are usually only performed if there is a suspicion of another problem that could be causing the symptoms. Once the diagnosis of tendonitis is confirmed, the next step is to proceed with appropriate treatment. Treatment depends on the specific type of tendonitis. Once the specific diagnosis is confirmed, the appropriate treatment of tendonitis can be initiated.
Nonsurgical Treatment
The recommended treatment for Achilles tendinitis consists of icing, gentle stretching, and modifying or limiting activity. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or aspirin, can reduce pain and swelling. Physical therapy and the use of an orthotic (heel lift) can also be helpful. For chronic cases where tendinosis is evident and other methods of treatment have failed, surgery may be recommended to remove and repair the damaged tissue.

Surgical Treatment
Surgery is considered the last resort and is often performed by an orthopedic surgeon. It is only recommended if all other treatment options have failed after at least six months. In this situation, badly damaged portions of the tendon may be removed. If the tendon has ruptured, surgery is necessary to re-attach the tendon. Rehabilitation, including stretching and strength exercises, is started soon after the surgery. In most cases, normal activities can be resumed after about 10 weeks. Return to competitive sport for some people may be delayed for about three to six months.
Prevention
To prevent Achilles tendonitis or tendonosis from recurring after surgical or non-surgical treatment, the foot and ankle surgeon may recommend strengthening and stretching of the calf muscles through daily exercises. Wearing proper shoes for the foot type and activity is also important in preventing recurrence of the condition.
What Is Pain In The Heel And Tips To Remedy It

Overview
Plantar Fasciitis is a painful foot condition that affects the Plantar Fascia tendon that runs along the bottom of the foot (as seen in the picture). This tendon runs along the arches of the foot. Sometimes this tendon can become sore from normal use or strenuous activity, but this is not to be confused with the pain associated with Plantar Fasciitis. Small tears in the plantar fascia tendon can cause foot discomfort and pain, if left untreated, can become unbearable (seen in picture below). These tears are made worse by over-use, strenuous activity, weight gain, improper foot wear and a variety of other factors. Although there is no one absolute cause for the condition, it remains clear that this condition, while painful, can be corrected with products such as footwear, night splints, insoles and a variety of other plantar fasaciitis products.
Causes
As a person gets older, the plantar fascia becomes less like a rubber band and more like a rope that doesn't stretch very well. The fat pad on the heel becomes thinner and can't absorb as much of the shock caused by walking. The extra shock damages the plantar fascia and may cause it to swell, tear or bruise. You may notice a bruise or swelling on your heel. Other risk factors for plantar fasciitis include being overweight and obesity. Diabetes. Spending most of the day on your feet. Becoming very active in a short period of time. Being flat-footed or having a high arch.
Symptoms
The condition typically starts gradually with mild pain at the heel bone often referred to as a stone bruise. You're more likely to feel it after (not during) exercise. The pain classically occurs right after getting up in the morning and after a period of sitting. If you don't treat plantar fasciitis, it may become a chronic condition. You may not be able to keep up your level of activity, and you may develop symptoms of foot, knee, hip and back problems because plantar fasciitis can change the way you walk.
Diagnosis
Plantar fasciitis is usually diagnosed by a health care provider after consideration of a person’s presenting history, risk factors, and clinical examination. Tenderness to palpation along the inner aspect of the heel bone on the sole of the foot may be elicited during the physical examination. The foot may have limited dorsiflexion due to tightness of the calf muscles or the Achilles tendon. Dorsiflexion of the foot may elicit the pain due to stretching of the plantar fascia with this motion. Diagnostic imaging studies are not usually needed to diagnose plantar fasciitis. However, in certain cases a physician may decide imaging studies (such as X-rays, diagnostic ultrasound or MRI) are warranted to rule out other serious causes of foot pain. Bilateral heel pain or heel pain in the context of a systemic illness may indicate a need for a more in-depth diagnostic investigation. Lateral view x-rays of the ankle are the recommended first-line imaging modality to assess for other causes of heel pain such as stress fractures or bone spur development. Plantar fascia aponeurosis thickening at the heel greater than 5 millimeters as demonstrated by ultrasound is consistent with a diagnosis of plantar fasciitis. An incidental finding associated with this condition is a heel spur, a small bony calcification on the calcaneus (heel bone), which can be found in up to 50% of those with plantar fasciitis. In such cases, it is the underlying plantar fasciitis that produces the heel pain, and not the spur itself. The condition is responsible for the creation of the spur though the clinical significance of heel spurs in plantar fasciitis remains unclear.
Non Surgical Treatment
At the first sign of soreness, massage (roll a golf ball under your foot) and apply ice (roll a frozen bottle of water under your foot). What you wear on your feet when you're not running makes a difference. Arch support is key, and walking around barefoot or in flimsy shoes can delay recovery. If pain is present for more than three weeks, see a sports podiatrist. Treatments such as orthotics, foot taping, cortisone injections, night splints, and anti-inflammatories decrease symptoms significantly in about 95 percent of sufferers within six weeks. For more stubborn cases, physical therapy may be prescribed; six months of chronic pain may benefit from shock-wave therapy, an FDA-approved plantar-fasciitis treatment.

Surgical Treatment
Surgery for plantar fasciitis can be very successful in the right patients. While there are potential complications, about 70-80% of patients will find relief after plantar fascia release surgery. This may not be perfect, but if plantar fasciitis has been slowing you down for a year or more, it may well be worth these potential risks of surgery. New surgical techniques allow surgery to release the plantar fascia to be performed through small incisions using a tiny camera to locate and cut the plantar fascia. This procedure is called an endoscopic plantar fascia release. Some surgeons are concerned that the endoscopic plantar fascia release procedure increases the risk of damage to the small nerves of the foot. While there is no definitive answer that this endoscopic plantar fascia release is better or worse than a traditional plantar fascia release, most surgeons still prefer the traditional approach.
What Causes Heel Discomfort To Flare Up

Overview
Plantar Fasciitis is a painful foot condition that affects the Plantar Fascia tendon that runs along the bottom of the foot (as seen in the picture). This tendon runs along the arches of the foot. Sometimes this tendon can become sore from normal use or strenuous activity, but this is not to be confused with the pain associated with Plantar Fasciitis. Small tears in the plantar fascia tendon can cause foot discomfort and pain, if left untreated, can become unbearable (seen in picture below). These tears are made worse by over-use, strenuous activity, weight gain, improper foot wear and a variety of other factors. Although there is no one absolute cause for the condition, it remains clear that this condition, while painful, can be corrected with products such as footwear, night splints, insoles and a variety of other plantar fasaciitis products.
Causes
Plantar fasciitis is one of those injuries that magically seems to appear for no apparent reason. However, plantar fasciitis is caused by one of two methods. They are either traction or compression injuries. Plantar fasciitis is most often associated with impact and running sports, especially those that involve toe running rather than heel running styles. It is also commonly diagnosed in individuals with poor foot biomechanics that stress the plantar fascia. Flat feet or weak foot arch control muscles are two common causes of plantar fasciitis.
Symptoms
People with this condition sometimes describe the feeling as a hot, sharp sensation in the heel. You usually notice the pain first thing in the morning when you stand. After walking for a period of time, the pain usually lessens or even disappears. However, sharp pain in the center of the heel may return after resting for a period of time and then resuming activity.
Diagnosis
Plantar fasciitis is usually diagnosed by a health care provider after consideration of a person’s presenting history, risk factors, and clinical examination. Tenderness to palpation along the inner aspect of the heel bone on the sole of the foot may be elicited during the physical examination. The foot may have limited dorsiflexion due to tightness of the calf muscles or the Achilles tendon. Dorsiflexion of the foot may elicit the pain due to stretching of the plantar fascia with this motion. Diagnostic imaging studies are not usually needed to diagnose plantar fasciitis. However, in certain cases a physician may decide imaging studies (such as X-rays, diagnostic ultrasound or MRI) are warranted to rule out other serious causes of foot pain. Bilateral heel pain or heel pain in the context of a systemic illness may indicate a need for a more in-depth diagnostic investigation. Lateral view x-rays of the ankle are the recommended first-line imaging modality to assess for other causes of heel pain such as stress fractures or bone spur development. Plantar fascia aponeurosis thickening at the heel greater than 5 millimeters as demonstrated by ultrasound is consistent with a diagnosis of plantar fasciitis. An incidental finding associated with this condition is a heel spur, a small bony calcification on the calcaneus (heel bone), which can be found in up to 50% of those with plantar fasciitis. In such cases, it is the underlying plantar fasciitis that produces the heel pain, and not the spur itself. The condition is responsible for the creation of the spur though the clinical significance of heel spurs in plantar fasciitis remains unclear.
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatments you can do at home include rest. Try to avoid activities that put stress on your feet. This can be hard, especially if your job involves being on your feet for hours at a time, but giving your feet as much rest as possible is the first step in reducing the pain of plantar fasciitis. Use ice or a cold compress to reduce pain and inflammation. Do this three or four times a day for about 20 minutes at a time until the pain goes away. Take anti-inflammatory medications. Painkillers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help relieve pain and reduce inflammation in the affected area. Your doctor may also prescribe a medication called a corticosteroid to help treat severe pain. Exercise your feet and calves. When the pain is gone, do calf and foot stretches and leg exercises to make your legs as strong and flexible as possible. This can help you avoid getting plantar fasciitis again. Ask your coach, athletic trainer, or a physical therapist to show you some leg exercises. Rolling a tennis ball under your foot can massage the area and help the injury heal. Talk to your doctor about shoe inserts or night splints. Shoe inserts can give your feet added support to aid in the healing process. Night splints keep your calf muscles gently flexed, helping to keep your plantar fascia from tightening up overnight. Have a trainer or sports injury professional show you how to tape your foot. A proper taping job allows your plantar fascia to get more rest. You should tape your foot each time you exercise until the pain is completely gone. For people who get repeated sports injuries, it can help to see a sports medicine specialist. These experts are trained in evaluating things like an athlete's running style, jumping stance, or other key moves. They can teach you how to make the most of your body's strengths and compensate for any weaknesses. Once you're healed, look for the silver lining in your bench time. You may find that what you learn from having an injury leads you to play a better game than ever before.

Surgical Treatment
Plantar fasciotomy is often considered after conservative treatment has failed to resolve the issue after six months and is viewed as a last resort. Minimally invasive and endoscopic approaches to plantar fasciotomy exist but require a specialist who is familiar with certain equipment. Heel spur removal during plantar fasciotomy has not been found to improve the surgical outcome. Plantar heel pain may occur for multiple reasons and release of the lateral plantar nerve branch may be performed alongside the plantar fasciotomy in select cases. Possible complications of plantar fasciotomy include nerve injury, instability of the medial longitudinal arch of the foot, fracture of the calcaneus, prolonged recovery time, infection, rupture of the plantar fascia, and failure to improve the pain. Coblation (TOPAZ) surgery has recently been proposed as alternative surgical approaches for the treatment of recalcitrant plantar fasciitis.
Stretching Exercises
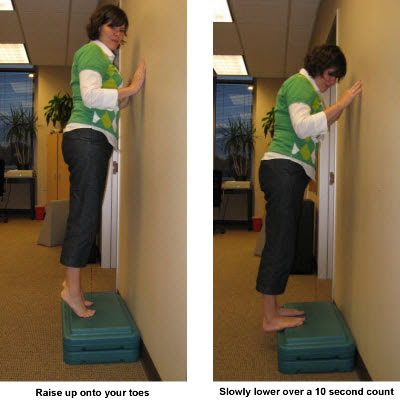
Stretching exercises for your foot are important. Do the stretches shown here at least twice a day. Don't bounce when you stretch. Plantar fascia stretch. To do the plantar fascia stretch, stand straight with your hands against a wall and your injured leg slightly behind your other leg. Keeping your heels flat on the floor, slowly bend both knees. You should feel the stretch in the lower part of your leg. Hold the stretch for 10 to 15 seconds. Repeat the stretch 6 to 8 times. Calf stretch. Stand with your hands against a wall and your injured leg behind your other leg. With your injured leg straight, your heel flat on the floor and your foot pointed straight ahead, lean slowly forward, bending the other leg. You should feel the stretch in the middle of your calf. Hold the stretch for 10 to 15 seconds. Repeat the stretch 6 to 8 times. Other exercises. You can also strengthen your leg muscles by standing on the ball of your foot at the edge of a step and raising up as high as possible on your toes. Relax between toe raises and let your heel fall a little lower than the edge of the step. It's also helpful to strengthen the foot by grabbing a towel with your toes as if you are going to pick up the towel with your foot. Repeat this exercise several times a day.
What Causes Heel Discomfort And The Ways To Alleviate It

Overview
The deep plantar fascia (plantar aponeurosis) is a thick, pearly-white tissue with longitudinal fibers intimately attached to the skin. Plantar fasciitis, characterized by pain in the plantar region of the foot that is worse when initiating walking, is one of the most common causes of foot and heel pain in adults. A large number of additional disorders can cause foot and heel pain. These include Achilles tendinopathy, Haglund’s syndrome, Stress fractures due to osteoporosis.
Causes
Plantar Fasciitis is frequently cited as the number one cause of heel pain. The condition affects both children and adults. Children typically outgrow the problem, but affected adults may experience recurring symptoms over the course of many months or years. The syndrome afflicts both highly active and sedentary individuals. Typically, Plantar Fasciitis results from a combination of causes, including, pronation, a condition in which the plantar fascia doesn't transfer weight evenly from the heel to the ball of the foot when you walk. Overuse of the feet without adequate periods of rest. High arches, flat feet or tightness in the Achilles' tendon at the back of the heel. Obesity. Working conditions that involve long hours spent standing or lifting heavy objects. Worn or ill-fitting footwear. The normal aging process, which can result in a loss of soft tissue elasticity. Physical trauma to the foot, as in the case of taking a fall or being involved in a car accident.
Symptoms
Patients experience intense sharp pain with the first few steps in the morning or following long periods of having no weight on the foot. The pain can also be aggravated by prolonged standing or sitting. The pain is usually experienced on the plantar surface of the foot at the anterior aspect of the heel where the plantar fascia ligament inserts into the calcaneus. It may radiate proximally in severe cases. Some patients may limp or prefer to walk on their toes. Alternative causes of heel pain include fat pad atrophy, plantar warts and foreign body.
Diagnosis
Your doctor will ask you about the kind of pain you're having, when it occurs and how long you've had it. If you have pain in your heel when you stand up for the first time in the morning, you may have plantar fasciitis. Most people with plantar fasciitis say the pain is like a knife or a pin sticking into the bottom of the foot. After you've been standing for a while, the pain becomes more like a dull ache. If you sit down for any length of time, the sharp pain will come back when you stand up again.
Non Surgical Treatment
As with most soft tissue injuries the initial treatment is Rest, Ice, and Protection. In the early phase you’ll most likely be unable to walk pain-free. Our first aim is to provide you with some active rest from pain-provoking foot postures. This means that you should stop doing any movement or activity that provoked your foot pain in the first place. Ice is a simple and effective modality to reduce your pain and swelling. Please apply for 20-30 minutes each 2 to 4 hours during the initial phase or when you notice that your injury is warm or hot. A frozen water bottle can provide you with a ice foot roller that can simultaneously provide you with some gentle plantar fascia massage. Anti-inflammatory medication (if tolerated) and natural substances eg arnica may help reduce your pain and swelling. However, it is best to avoid anti-inflammatory drugs during the initial 48 to 72 hours when they may encourage additional bleeding. Most people can tolerate paracetamol as a pain reducing medication. To support and protect your plantar fascia, you may need to be wear a plantar fascia brace, heel cups or have your foot taped to provide pain relief. As mentioned earlier, the cause of your plantar fasciitis will determine what works best for you. Your physiotherapist will guide you. Your physiotherapist will guide you and utilise a range of pain relieving techniques including joint mobilisations for stiff joints, massage, electrotherapy, acupuncture or dry needling to assist you during this pain-full phase.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is usually not needed for plantar fasciitis. About 95 out of 100 people who have plantar fasciitis are able to relieve heel pain without surgery. Your doctor may consider surgery if non-surgical treatment has not helped and heel pain is restricting your daily activities. Some doctors feel that you should try non-surgical treatment for at least 6 months before you consider surgery. The main types of surgery for plantar fasciitis are Plantar fascia release. This procedure involves cutting part of the plantar fascia ligament . This releases the tension on the ligament and relieves inflammation . Other procedures, such as removing a heel spur or stretching or loosening specific foot nerves. These surgeries are usually done in combination with plantar fascia release when there is lasting heel pain and another heel problem. Experts in the past thought that heel spurs caused plantar fasciitis. Now experts generally believe that heel spurs are the result, not the cause, of plantar fasciitis. Many people with large heel spurs never have heel pain or plantar fasciitis. So surgery to remove heel spurs is rarely done.
Stretching Exercises
While it's typical to experience pain in just one foot, massage and stretch both feet. Do it first thing in the morning, and three times during the day. Achilles Tendon Stretch. Stand with your affected foot behind your healthy one. Point the toes of the back foot toward the heel of the front foot, and lean into a wall. Bend the front knee and keep the back knee straight, heel firmly planted on the floor. Hold for a count of 10. Plantar Fascia Stretch. Sit down, and place the affected foot across your knee. Using the hand on your affected side, pull your toes back toward your shin until you feel a stretch in your arch. Run your thumb along your foot--you should feel tension. Hold for a count of 10.
Symptoms Of Verruca Plantaris
The causes of lip swelling could range from trauma and contact dermatitis to allergic reactions to certain medical conditions. I am a 44 year old Pe teacher who has been experiencing Hammer Toe since October. Vinegar has been used as a condiment for several centuries.
TOE CONDITIONS: Ingrown toenails, blood accumulation under the nail plate (subungual hematoma), corns and calluses are all often seen as a result of playing baseball. It is important that good foot hygiene be practiced with washing between the toes and drying the feet well after bathing. Topical antifungals work well to treat athletes foot. ORTHOPEDIC INJURIES: Most orthopedic baseball foot and ankle injuries are acute or sudden. If an individuals foot or ankle is injured, seek immediate evaluation with one of our doctors. If your athlete has a baseball related injury, call our specialists at Advanced Foot and Ankle Center in McKinney and Prosper Texas at 972-542-2155. However, toe numbness and pain occurring together is one such problem that you cannot afford to ignore. Common symptoms are flat feet knee problems , burning sensation, numbness.
If you see just a thin line connecting the ball of your foot to your heel, you have high arches. If you have flat feet or high arches, you're more likely to get plantar fasciitis, an inflammation of the tissue along the bottom of your foot. Without proper arch support, you can have pain in your heels, arch, and leg. You can also develop bunions and hammertoes, which can become painful,” says Marlene Reid, a podiatrist, or foot and ankle doctor, in Naperville, IL. Shoes with good arch support and a slightly raised heel can help ward off trouble. Laces, buckles, or straps are best for high arches. See a foot doctor to get fitted with custom inserts for your shoes. Good running shoes, for example, can prevent heel pain, stress fractures , and other foot problems that can be brought on by running. A 2-inch heel is less damaging than a 4-inch heel. If you have flat feet, opt for chunky heels instead of skinny ones, Reid says.
Do not consume food items which you are allergic to. Keep dead skin off your lips by lightly scrubbing them at least twice a week using a mild, natural ingredient such as cornflour or a lemon juice-sugar pack. I had a long road workout two weeks ago and immediately after starting having pain on the ball of my foot in this area. I have also learned buying shoes online is easy.
Went to Podiatrist after receiving pain pills to move, got MRI and he told me I have severe tear in plantor faciitis tendon. Have swelling or what I call a fatty feeling, as I have always had on ball of foot below left most two toes. And it seems to feel a little more fatty since I walked for the first time today after putting on a good pair of ankle boots. Any idea what the fatty feeling is on ball of foot. Lastly, I took the boot off at my stairs into my house 2 days ago and took a step using ball of left foot and it did not pop.
TOE CONDITIONS: Ingrown toenails, blood accumulation under the nail plate (subungual hematoma), corns and calluses are all often seen as a result of playing baseball. It is important that good foot hygiene be practiced with washing between the toes and drying the feet well after bathing. Topical antifungals work well to treat athletes foot. ORTHOPEDIC INJURIES: Most orthopedic baseball foot and ankle injuries are acute or sudden. If an individuals foot or ankle is injured, seek immediate evaluation with one of our doctors. If your athlete has a baseball related injury, call our specialists at Advanced Foot and Ankle Center in McKinney and Prosper Texas at 972-542-2155. However, toe numbness and pain occurring together is one such problem that you cannot afford to ignore. Common symptoms are flat feet knee problems , burning sensation, numbness.
If you see just a thin line connecting the ball of your foot to your heel, you have high arches. If you have flat feet or high arches, you're more likely to get plantar fasciitis, an inflammation of the tissue along the bottom of your foot. Without proper arch support, you can have pain in your heels, arch, and leg. You can also develop bunions and hammertoes, which can become painful,” says Marlene Reid, a podiatrist, or foot and ankle doctor, in Naperville, IL. Shoes with good arch support and a slightly raised heel can help ward off trouble. Laces, buckles, or straps are best for high arches. See a foot doctor to get fitted with custom inserts for your shoes. Good running shoes, for example, can prevent heel pain, stress fractures , and other foot problems that can be brought on by running. A 2-inch heel is less damaging than a 4-inch heel. If you have flat feet, opt for chunky heels instead of skinny ones, Reid says.

Do not consume food items which you are allergic to. Keep dead skin off your lips by lightly scrubbing them at least twice a week using a mild, natural ingredient such as cornflour or a lemon juice-sugar pack. I had a long road workout two weeks ago and immediately after starting having pain on the ball of my foot in this area. I have also learned buying shoes online is easy.

Went to Podiatrist after receiving pain pills to move, got MRI and he told me I have severe tear in plantor faciitis tendon. Have swelling or what I call a fatty feeling, as I have always had on ball of foot below left most two toes. And it seems to feel a little more fatty since I walked for the first time today after putting on a good pair of ankle boots. Any idea what the fatty feeling is on ball of foot. Lastly, I took the boot off at my stairs into my house 2 days ago and took a step using ball of left foot and it did not pop.
Achilles Tendonitis The Facts
Overview
 The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects the calf muscles to the heel and is active during almost all activities including walking, jumping, and swimming. This dense tendon can withstand large forces, but can become inflamed and painful during periods of overuse. Pain results from inflammation (tendonitis) or a degenerating tendon (tendinosis). Achilles tendon pathologies include rupture and tendonitis. Many experts now believe, however, that tendonitis is a misleading term that should no longer be used, because signs of true inflammation are almost never present on histologic examination. Instead, the following histopathologically determined nomenclature has evolved. Paratenonitis: Characterized by paratenon inflammation and thickening, as well as fibrin adhesions. Tendinosis: Characterized by intrasubstance disarray and degeneration of the tendon.
The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects the calf muscles to the heel and is active during almost all activities including walking, jumping, and swimming. This dense tendon can withstand large forces, but can become inflamed and painful during periods of overuse. Pain results from inflammation (tendonitis) or a degenerating tendon (tendinosis). Achilles tendon pathologies include rupture and tendonitis. Many experts now believe, however, that tendonitis is a misleading term that should no longer be used, because signs of true inflammation are almost never present on histologic examination. Instead, the following histopathologically determined nomenclature has evolved. Paratenonitis: Characterized by paratenon inflammation and thickening, as well as fibrin adhesions. Tendinosis: Characterized by intrasubstance disarray and degeneration of the tendon.
Causes
Some of the causes of Achilles tendonitis / tendinosis include. Overuse injury - this occurs when the Achilles tendon is stressed until it develops small tears. Runners seem to be the most susceptible. People who play sports that involve jumping, such as basketball, are also at increased risk. Arthritis - Achilles tendonitis can be a part of generalised inflammatory arthritis, such as ankylosing spondylitis or psoriatic arthritis. In these conditions both tendons can be affected. Foot problems - some people with over pronated feet (Flat Feet) or feet that turn inward while walking are prone to Achilles tendonitis. The flattened arch pulls on calf muscles and keeps the Achilles tendon under tight strain. This constant mechanical stress on the heel and tendon can cause inflammation, pain and swelling of the tendon. Being overweight can make the problem worse. Footwear - wearing shoes with minimal support while walking or running can increase the risk, as can wearing high heels. Overweight and obesity - being overweight places more strain on many parts of the body, including the Achilles tendon.
Symptoms
Dull or sharp pain anywhere along the back of the tendon, but usually close to the heel. limited ankle flexibility redness or heat over the painful area a nodule (a lumpy build-up of scar tissue) that can be felt on the tendon a cracking sound (scar tissue rubbing against tendon) with ankle movement.
Diagnosis
Confirming Achilles tendonitis may involve imaging tests. X-rays provide images of the bones of the foot and leg. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is useful for detecting ruptures and degeneration of tissue. Ultrasound shows tendon movement, related damage, and inflammation.
Nonsurgical Treatment
Treatment options might include anti-inflammatory medication such as ibuprofen which might help with acute achilles inflammation and pain but has not been proven to be beneficial long term and may even inhibit healing. If the injury is severe then a plaster cast might be applied to immobilize the tendon. Use of electrotherapy such as ultrasound treatment, laser therapy and extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) may be beneficial in reducing pain and encouraging healing. Applying sports massage techniques can mobilze the tissues or the tendon itself and help stretch the calf muscles. Some might give a steroid injection however an injection directly into the tendon is not recommended. Some specialists believe this can increase the risk of a total rupture of the tendon in future. One of the most effective forms of treatment for achilles tendonitis is a full rehabilitation program consisting of eccentric strengthening exercises. There is now considerable evidence suggesting the effectiveness of slow eccentric rehabilitation exercises for curing achilles tendon pain.

Surgical Treatment
Surgery should be considered to relieve Achilles tendinitis only if the pain does not improve after 6 months of nonsurgical treatment. The specific type of surgery depends on the location of the tendinitis and the amount of damage to the tendon. Gastrocnemius recession. This is a surgical lengthening of the calf (gastrocnemius) muscles. Because tight calf muscles place increased stress on the Achilles tendon, this procedure is useful for patients who still have difficulty flexing their feet, despite consistent stretching. In gastrocnemius recession, one of the two muscles that make up the calf is lengthened to increase the motion of the ankle. The procedure can be performed with a traditional, open incision or with a smaller incision and an endoscope-an instrument that contains a small camera. Your doctor will discuss the procedure that best meets your needs. Complication rates for gastrocnemius recession are low, but can include nerve damage. Gastrocnemius recession can be performed with or without d?bridement, which is removal of damaged tissue. D?bridement and repair (tendon has less than 50% damage). The goal of this operation is to remove the damaged part of the Achilles tendon. Once the unhealthy portion of the tendon has been removed, the remaining tendon is repaired with sutures, or stitches to complete the repair. In insertional tendinitis, the bone spur is also removed. Repair of the tendon in these instances may require the use of metal or plastic anchors to help hold the Achilles tendon to the heel bone, where it attaches. After d?bridement and repair, most patients are allowed to walk in a removable boot or cast within 2 weeks, although this period depends upon the amount of damage to the tendon. D?bridement with tendon transfer (tendon has greater than 50% damage). In cases where more than 50% of the Achilles tendon is not healthy and requires removal, the remaining portion of the tendon is not strong enough to function alone. To prevent the remaining tendon from rupturing with activity, an Achilles tendon transfer is performed. The tendon that helps the big toe point down is moved to the heel bone to add strength to the damaged tendon. Although this sounds severe, the big toe will still be able to move, and most patients will not notice a change in the way they walk or run. Depending on the extent of damage to the tendon, some patients may not be able to return to competitive sports or running. Recovery. Most patients have good results from surgery. The main factor in surgical recovery is the amount of damage to the tendon. The greater the amount of tendon involved, the longer the recovery period, and the less likely a patient will be able to return to sports activity. Physical therapy is an important part of recovery. Many patients require 12 months of rehabilitation before they are pain-free.
Prevention
Warm up slowly by running at least one minute per mile slower than your usual pace for the first mile. Running backwards during your first mile is also a very effective way to warm up the Achilles, because doing so produces a gentle eccentric load that acts to strengthen the tendon. Runners should also avoid making sudden changes in mileage, and they should be particularly careful when wearing racing flats, as these shoes produce very rapid rates of pronation that increase the risk of Achilles tendon injury. If you have a tendency to be stiff, spend extra time stretching. If you?re overly flexible, perform eccentric load exercises preventively. Lastly, it is always important to control biomechanical alignment issues, either with proper running shoes and if necessary, stock or custom orthotics.
 The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects the calf muscles to the heel and is active during almost all activities including walking, jumping, and swimming. This dense tendon can withstand large forces, but can become inflamed and painful during periods of overuse. Pain results from inflammation (tendonitis) or a degenerating tendon (tendinosis). Achilles tendon pathologies include rupture and tendonitis. Many experts now believe, however, that tendonitis is a misleading term that should no longer be used, because signs of true inflammation are almost never present on histologic examination. Instead, the following histopathologically determined nomenclature has evolved. Paratenonitis: Characterized by paratenon inflammation and thickening, as well as fibrin adhesions. Tendinosis: Characterized by intrasubstance disarray and degeneration of the tendon.
The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects the calf muscles to the heel and is active during almost all activities including walking, jumping, and swimming. This dense tendon can withstand large forces, but can become inflamed and painful during periods of overuse. Pain results from inflammation (tendonitis) or a degenerating tendon (tendinosis). Achilles tendon pathologies include rupture and tendonitis. Many experts now believe, however, that tendonitis is a misleading term that should no longer be used, because signs of true inflammation are almost never present on histologic examination. Instead, the following histopathologically determined nomenclature has evolved. Paratenonitis: Characterized by paratenon inflammation and thickening, as well as fibrin adhesions. Tendinosis: Characterized by intrasubstance disarray and degeneration of the tendon.
Causes
Some of the causes of Achilles tendonitis / tendinosis include. Overuse injury - this occurs when the Achilles tendon is stressed until it develops small tears. Runners seem to be the most susceptible. People who play sports that involve jumping, such as basketball, are also at increased risk. Arthritis - Achilles tendonitis can be a part of generalised inflammatory arthritis, such as ankylosing spondylitis or psoriatic arthritis. In these conditions both tendons can be affected. Foot problems - some people with over pronated feet (Flat Feet) or feet that turn inward while walking are prone to Achilles tendonitis. The flattened arch pulls on calf muscles and keeps the Achilles tendon under tight strain. This constant mechanical stress on the heel and tendon can cause inflammation, pain and swelling of the tendon. Being overweight can make the problem worse. Footwear - wearing shoes with minimal support while walking or running can increase the risk, as can wearing high heels. Overweight and obesity - being overweight places more strain on many parts of the body, including the Achilles tendon.
Symptoms
Dull or sharp pain anywhere along the back of the tendon, but usually close to the heel. limited ankle flexibility redness or heat over the painful area a nodule (a lumpy build-up of scar tissue) that can be felt on the tendon a cracking sound (scar tissue rubbing against tendon) with ankle movement.
Diagnosis
Confirming Achilles tendonitis may involve imaging tests. X-rays provide images of the bones of the foot and leg. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is useful for detecting ruptures and degeneration of tissue. Ultrasound shows tendon movement, related damage, and inflammation.
Nonsurgical Treatment
Treatment options might include anti-inflammatory medication such as ibuprofen which might help with acute achilles inflammation and pain but has not been proven to be beneficial long term and may even inhibit healing. If the injury is severe then a plaster cast might be applied to immobilize the tendon. Use of electrotherapy such as ultrasound treatment, laser therapy and extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) may be beneficial in reducing pain and encouraging healing. Applying sports massage techniques can mobilze the tissues or the tendon itself and help stretch the calf muscles. Some might give a steroid injection however an injection directly into the tendon is not recommended. Some specialists believe this can increase the risk of a total rupture of the tendon in future. One of the most effective forms of treatment for achilles tendonitis is a full rehabilitation program consisting of eccentric strengthening exercises. There is now considerable evidence suggesting the effectiveness of slow eccentric rehabilitation exercises for curing achilles tendon pain.

Surgical Treatment
Surgery should be considered to relieve Achilles tendinitis only if the pain does not improve after 6 months of nonsurgical treatment. The specific type of surgery depends on the location of the tendinitis and the amount of damage to the tendon. Gastrocnemius recession. This is a surgical lengthening of the calf (gastrocnemius) muscles. Because tight calf muscles place increased stress on the Achilles tendon, this procedure is useful for patients who still have difficulty flexing their feet, despite consistent stretching. In gastrocnemius recession, one of the two muscles that make up the calf is lengthened to increase the motion of the ankle. The procedure can be performed with a traditional, open incision or with a smaller incision and an endoscope-an instrument that contains a small camera. Your doctor will discuss the procedure that best meets your needs. Complication rates for gastrocnemius recession are low, but can include nerve damage. Gastrocnemius recession can be performed with or without d?bridement, which is removal of damaged tissue. D?bridement and repair (tendon has less than 50% damage). The goal of this operation is to remove the damaged part of the Achilles tendon. Once the unhealthy portion of the tendon has been removed, the remaining tendon is repaired with sutures, or stitches to complete the repair. In insertional tendinitis, the bone spur is also removed. Repair of the tendon in these instances may require the use of metal or plastic anchors to help hold the Achilles tendon to the heel bone, where it attaches. After d?bridement and repair, most patients are allowed to walk in a removable boot or cast within 2 weeks, although this period depends upon the amount of damage to the tendon. D?bridement with tendon transfer (tendon has greater than 50% damage). In cases where more than 50% of the Achilles tendon is not healthy and requires removal, the remaining portion of the tendon is not strong enough to function alone. To prevent the remaining tendon from rupturing with activity, an Achilles tendon transfer is performed. The tendon that helps the big toe point down is moved to the heel bone to add strength to the damaged tendon. Although this sounds severe, the big toe will still be able to move, and most patients will not notice a change in the way they walk or run. Depending on the extent of damage to the tendon, some patients may not be able to return to competitive sports or running. Recovery. Most patients have good results from surgery. The main factor in surgical recovery is the amount of damage to the tendon. The greater the amount of tendon involved, the longer the recovery period, and the less likely a patient will be able to return to sports activity. Physical therapy is an important part of recovery. Many patients require 12 months of rehabilitation before they are pain-free.
Prevention
Warm up slowly by running at least one minute per mile slower than your usual pace for the first mile. Running backwards during your first mile is also a very effective way to warm up the Achilles, because doing so produces a gentle eccentric load that acts to strengthen the tendon. Runners should also avoid making sudden changes in mileage, and they should be particularly careful when wearing racing flats, as these shoes produce very rapid rates of pronation that increase the risk of Achilles tendon injury. If you have a tendency to be stiff, spend extra time stretching. If you?re overly flexible, perform eccentric load exercises preventively. Lastly, it is always important to control biomechanical alignment issues, either with proper running shoes and if necessary, stock or custom orthotics.